Careers That Are Growing Faster Because of Data & Technology

In today’s digital-first world, Data and Technology are no longer optional skills — they are the backbone of modern businesses. From startups to global enterprises, companies are using data-driven decisions and advanced technology to grow faster, smarter, and more efficiently. As a result, careers powered by data and technology are growing at an unprecedented speed and offer exciting opportunities for students, freshers, and working professionals. This blog will help you understand: Why Data & Technology Are So Important Today: Powering the Digital Age Introduction: Living in a Data-Driven World We are living in an era where almost every action we perform leaves a digital footprint. From browsing websites and using mobile applications to online shopping, digital payments, social media engagement, and even smart home devices, data is constantly being generated. This massive flow of information has transformed how organizations operate, how governments make decisions, and how individuals interact with technology. Data and technology are no longer optional tools; they have become the foundation of modern business, innovation, and social development. The combination of data and technology enables organizations to gain deep insights, automate complex processes, enhance customer experiences, and remain competitive in fast-changing markets. Companies that understand how to collect, analyze, and apply data effectively are more likely to grow faster, reduce operational risks, and make informed strategic decisions. This is why data literacy and technological skills are now considered essential across industries and professions. Understanding the Role of Data in the Modern Economy What Is Data and Why Does It Matter? Data refers to raw facts and information generated through digital interactions, sensors, transactions, customer feedback, and online activities. While raw data alone may seem meaningless, when it is processed and analyzed using technology, it becomes valuable intelligence that helps organizations understand patterns, trends, and user behavior. In today’s digital economy, data has become one of the most valuable assets. Companies such as e-commerce platforms, social media networks, financial institutions, and healthcare providers rely heavily on data to improve services, personalize user experiences, and optimize internal operations. Data-driven organizations are able to make smarter decisions based on evidence rather than assumptions, leading to improved performance and sustainable growth. Data as a Strategic Business Resource Unlike traditional resources such as machinery or physical infrastructure, data can be reused, refined, and expanded over time. Businesses now treat data as a strategic resource that helps them identify market opportunities, reduce inefficiencies, and gain a competitive advantage. Organizations that invest in data analytics tools and skilled professionals can convert complex information into actionable insights that directly impact profitability and customer satisfaction. How Technology Converts Data into Meaningful Insights The Role of Advanced Technologies Technology plays a critical role in transforming raw data into useful knowledge. Tools such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, machine learning, big data platforms, and automation systems enable organizations to process large volumes of information quickly and accurately. These technologies allow businesses to extract patterns, predict outcomes, and generate insights that would be impossible to achieve through manual methods. For example, machine learning algorithms can analyze customer purchase behavior to recommend products, while predictive analytics can help companies forecast demand and manage inventory efficiently. Cloud platforms make it possible to store massive datasets securely and access them from anywhere in the world, supporting remote work and global collaboration. Automation and Real-Time Decision Making Modern technology also enables real-time data processing and automation. Businesses can monitor performance metrics instantly, detect issues early, and respond to changes in the market faster than ever before. Automated systems reduce human error, increase operational efficiency, and allow employees to focus on strategic and creative tasks instead of repetitive manual work. Improving Customer Experience Through Data and Technology Understanding Customer Behavior One of the biggest advantages of using data is the ability to understand customer behavior in detail. Businesses can analyze browsing patterns, purchase history, feedback, and engagement metrics to gain insights into customer preferences and expectations. This helps organizations create personalized experiences that build stronger relationships and increase brand loyalty. Personalization has become a key factor in customer satisfaction. Whether it is customized product recommendations, targeted marketing campaigns, or personalized support services, data-driven strategies allow companies to deliver relevant content and offers that match individual customer needs. Enhancing Customer Engagement and Trust Technology also enables businesses to communicate more effectively with customers through chatbots, CRM systems, and automated support tools. These solutions provide faster response times, consistent service quality, and better issue resolution. When customers receive timely and accurate support, their trust in the brand increases, leading to long-term relationships and repeat business. Driving Business Growth and Profitability Data-Driven Decision Making Traditional business decisions were often based on intuition or past experience. Today, organizations rely on data analytics to support decision-making processes. By analyzing market trends, consumer demand, and operational performance, companies can make informed choices that reduce risks and improve outcomes. Data-driven strategies help businesses identify new opportunities, optimize pricing models, and improve resource allocation. This results in higher productivity, better financial performance, and stronger competitive positioning in the market. Optimizing Operations and Reducing Costs Technology enables businesses to streamline operations through automation and process optimization. Supply chain management systems, inventory tracking tools, and enterprise software platforms help organizations reduce waste, minimize delays, and improve overall efficiency. By leveraging data insights, companies can identify bottlenecks and implement improvements that save time and money. The Impact of Data and Technology Across Industries Information Technology and Software Development The IT sector relies heavily on data and advanced technologies to develop innovative software solutions, manage networks, and ensure cybersecurity. Data analytics helps IT professionals monitor system performance, detect security threats, and improve user experience. Cloud computing and artificial intelligence have further expanded the possibilities of digital transformation. Healthcare and Medical Innovation In healthcare, data and technology have revolutionized patient care and medical research. Electronic health records, wearable devices, and diagnostic tools generate valuable patient data that helps doctors make accurate diagnoses and develop personalized treatment plans. Predictive analytics is also being used to identify disease patterns
Choosing the Right Skill Path for Long-Term Career Success

Your Ultimate Guide to Making Smart, Future-Proof Career Decisions In today’s fast-moving and highly competitive world, choosing the right career path is no longer a simple decision driven by passion alone. While interest and motivation still matter, long-term career success now depends on how informed, strategic, and future-ready your choices are. The professional landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace, and the skills you choose to develop today will directly influence your opportunities, stability, and growth tomorrow. Digital transformation, automation, and global connectivity have reshaped how industries operate and how talent is evaluated. Jobs that were once secure are being redefined, while entirely new roles are emerging across technology, analytics, sustainability, and digital business. In this environment, skills have become the true currency of career growth. Choosing wisely can open doors to global opportunities, while poor decisions can limit progress despite hard work. Why Choosing the Right Skill Path Matters More Than Ever The Career Decisions That Quietly Shape Your Entire Future Every major turning point in life is often defined not by one dramatic moment, but by a series of small, consistent decisions. Career choices work the same way. The skills you choose to learn today silently influence where you will stand five, ten, or even twenty years from now. They determine not just your income, but your confidence, relevance, freedom, and long-term satisfaction. In a world where industries are transforming faster than ever before, choosing the right skill path has become less of an option and more of a necessity. Unlike earlier generations, where one degree could support an entire career, today’s professionals must think dynamically. Skills are no longer static assets; they are living tools that must evolve with market needs. The right skill path can unlock opportunities, while the wrong one can quietly limit growth—even for highly hardworking individuals. Understanding the Shift: How the Job Market Is Being Redefined From Stable Roles to Skill-Driven Careers The global job market is undergoing a historic transformation. Traditional roles that once offered long-term stability are gradually giving way to flexible, skill-centric careers. Employers today are less focused on titles and more focused on capabilities. What you can do now matters far more than what you studied years ago. Technological advancement, globalization, and digital adoption have accelerated this shift. Automation is replacing repetitive tasks, while innovation is creating entirely new categories of work. As a result, professionals who continuously upgrade their skills are moving ahead, while those who rely solely on past qualifications often struggle to stay relevant. Alignment with Market Demand: The Foundation of a Strong Career Why Demand-Driven Skills Create Long-Term Value Choosing a skill path aligned with market demand ensures that your efforts translate into real opportunities. Industries invest in skills that solve current and future problems, and professionals who possess those skills naturally become valuable assets. In 2026 and beyond, sectors such as artificial intelligence, digital analytics, automation, cybersecurity, renewable energy, and advanced software development are shaping the global workforce. Roles like AI and machine learning specialists, data scientists, cloud engineers, digital strategists, and automation experts are no longer niche positions. They are becoming core functions across industries—from healthcare and finance to manufacturing and retail. This rise reflects where businesses are allocating budgets, building infrastructure, and planning for the future. When your skills align with these demands, you are not chasing jobs. Jobs begin to find you. Job Security and Growth in an Uncertain World How the Right Skills Protect You Against Disruption Job security today does not come from staying in one company for decades. It comes from being employable across companies, industries, and even countries. Professionals with in-demand skills enjoy a level of security that goes beyond a single role—they carry their value with them wherever they go. Global employment projections indicate that while some traditional jobs may decline, millions of new roles are expected to emerge by 2030. This shift does not signal job loss; it signals job transformation. New opportunities are being created faster than old ones are disappearing—but only for those who are prepared. When you invest in the right skill path, you position yourself on the growth side of this transformation. You become part of the workforce that is expanding, not shrinking. This leads to higher earning potential, faster promotions, and greater negotiating power throughout your career. Adaptation to Change: The New Career Superpower Why Learning Agility Matters More Than Experience Industries no longer operate on fixed models. Technology, consumer behavior, and global trends continuously reshape how businesses function. Skills that were relevant five years ago may already be outdated today. In this environment, adaptability is no longer optional—it is essential. Choosing the right skill path means choosing skills that evolve rather than expire. Fields like AI, data, digital marketing, and automation are not static disciplines. They constantly update, encouraging professionals to grow alongside them. This continuous learning keeps your mindset flexible and your profile competitive. Professionals who adapt quickly are not threatened by change—they leverage it. They move confidently through transitions, whether it’s a new role, a new industry, or a new market altogether. Financial Stability and Career Sustainability How Skills Translate into Income and Independence Financial growth is a natural outcome of valuable skills. When your expertise solves real business problems, organizations are willing to pay a premium for it. The right skill path often leads to multiple income streams—full-time roles, consulting, freelancing, or entrepreneurial ventures. Moreover, skill-based careers reduce dependency on a single employer. This independence offers greater control over career decisions, work-life balance, and long-term planning. Professionals with strong, relevant skills can adapt their careers around life changes instead of being constrained by them. Over time, this stability compounds—not just financially, but emotionally. Confidence grows when you know your skills will remain valuable regardless of market fluctuations. Personal Fulfillment and Professional Confidence When Growth Aligns with Purpose A well-chosen skill path does more than secure jobs; it builds confidence and fulfillment. Learning meaningful skills creates a sense of progress and control over your future. You
How Consulting-Based Learning Prepares You for Real-World Projects

Bridging the Gap Between Classroom Knowledge and Industry Practice Traditional classroom learning plays an important role in building a strong foundation of concepts, theories, and frameworks. Students learn models, methodologies, and best practices that explain how businesses, markets, and organizations work. However, one of the biggest challenges students face is applying this theoretical knowledge to real-world situations. This is where consulting-based learning becomes a powerful bridge between academics and industry practice. Consulting-based learning exposes students to real business problems rather than hypothetical case studies. Instead of solving predefined textbook questions, learners work on live projects where challenges are often complex, dynamic, and unclear. This experience helps students understand that real-world problems rarely have one “correct” answer. They learn to analyze situations, identify root causes, and design practical solutions that align with business goals, budgets, and timelines. By working on consulting-style projects, students begin to think and act like professionals. They apply classroom concepts such as market analysis, strategy formulation, data interpretation, and process optimization in real scenarios. This hands-on application strengthens their understanding and helps them retain knowledge more effectively compared to passive learning methods. It also teaches them how to adapt theories when real-world constraints come into play. Another major advantage of consulting-based learning is exposure to industry expectations. Students learn how to communicate with stakeholders, present findings clearly, and justify their recommendations with data and insights. They gain experience in teamwork, client interaction, deadline management, and professional documentation—skills that are often difficult to develop in a traditional academic environment. Most importantly, consulting-based learning builds confidence. When students successfully contribute to real projects, they realize their knowledge has practical value. This confidence prepares them to transition smoothly from classroom learning to professional roles, reducing the gap between education and employment. As a result, graduates enter the workforce not just with theoretical knowledge, but with real-world experience that employers highly value. Hands-On Experience That Shapes Future Professionals Hands-on experience is one of the most valuable aspects of consulting-based learning, as it allows students to move beyond theory and actively engage in real-world problem-solving. Instead of only learning what to do, students learn how to do it by working on live projects that reflect actual industry challenges. This practical exposure helps shape students into confident, capable, and industry-ready professionals. Through consulting-based learning, students are involved in every stage of a project—from understanding the client’s problem and conducting research to analyzing data and presenting actionable solutions. This end-to-end exposure gives them a realistic understanding of how professional projects operate. It also helps them develop a structured approach to solving problems, a skill that is essential across all industries. Hands-on projects encourage critical thinking and decision-making. Students must evaluate multiple options, assess risks, and justify their recommendations based on real constraints such as time, budget, and resources. This process strengthens their analytical abilities and teaches them to make informed decisions rather than relying solely on theoretical assumptions. In addition to technical knowledge, consulting-based learning builds essential soft skills. Students learn how to collaborate with team members, communicate ideas clearly, handle feedback, and adapt to changing project requirements. These skills are crucial for professional success and are often what differentiate high-performing individuals in the workplace. Most importantly, hands-on experience helps students discover their strengths and career interests. By working on real projects, they gain clarity about the roles and responsibilities they enjoy, whether it is strategy, analysis, client communication, or execution. This self-awareness, combined with practical experience, shapes future professionals who are not only skilled but also confident and career-focused. Turning Theory into Action Through Real-World Consulting One of the biggest challenges in traditional education is translating theoretical knowledge into practical application. While concepts, frameworks, and models provide essential understanding, their true value is realized only when they are applied in real-world situations. Real-world consulting bridges this gap by giving learners the opportunity to implement theory in dynamic, practical environments. Through consulting-based learning, students actively apply academic concepts such as business strategy, market research, data analysis, and problem-solving frameworks to actual business challenges. Instead of working on hypothetical examples, they engage with real clients, real data, and real constraints. This hands-on application helps students understand how theoretical ideas evolve when faced with practical limitations and real-world complexity. Real-world consulting also teaches adaptability. In professional settings, challenges are rarely well-defined, and information may be incomplete or constantly changing. Students learn to refine their approach, adjust strategies, and think critically when theoretical models do not fit perfectly. This ability to adapt theory to practice is a crucial skill that prepares students for the unpredictable nature of professional work. Additionally, consulting projects emphasize accountability and results. Students are responsible for delivering actionable insights and measurable outcomes, not just academic answers. This sense of responsibility encourages deeper engagement, stronger ownership of work, and a results-oriented mindset that employers highly value. By turning theory into action through real-world consulting, learners gain practical confidence and professional competence. They graduate not only with conceptual knowledge but also with the ability to apply that knowledge effectively in real business environments, making them better prepared for real-world projects and long-term career success. Learning by Solving Actual Business Challenges Consulting-based learning allows students to gain knowledge by working on real business problems rather than theoretical examples. This approach helps learners understand how businesses function in practical environments and prepares them for real-world responsibilities. From Case Studies to Career-Ready Skills Case studies have long been an important part of academic learning, helping students understand business scenarios, strategies, and decision-making processes. They introduce learners to real-life situations in a structured way and encourage analytical thinking. However, while case studies are valuable, they often remain limited to discussion and theoretical solutions. Consulting-based learning takes this a step further by transforming case-based understanding into practical, career-ready skills. Through consulting-oriented projects, students move beyond analyzing past situations to actively working on current and evolving business challenges. Instead of simply discussing what a company should do, learners are involved in researching, analyzing, and recommending solutions that can be implemented
How Non-Tech Students Can Enter Data Science Without Coding Fear

A Beginner-Friendly Roadmap with a Practical Learning Approach Data Science has become one of the most in-demand career options today. However, many students from non-technical backgrounds (Arts, Commerce, Management, Humanities) hesitate to enter this field because of one common fear — coding. The good news is: You do not need to be an engineer or a hardcore coder to start a career in Data Science. This guide explains how non-tech students can confidently enter Data Science using a step-by-step, practical, and beginner-friendly approach. 1. What Is Data Science? Data Science is the process of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data in order to make smart and informed decisions.In today’s digital world, almost everything we do creates data — from online shopping and social media to banking, healthcare, and education. Data Science helps organizations understand this data and use it in a meaningful way. Instead of making decisions based on guesswork, companies use Data Science to find patterns, trends, and insights hidden inside large amounts of data. Analyzing Sales Data to Increase Profit Analyzing sales data means carefully studying information related to a company’s sales, such as how much was sold, when it was sold, and which products performed best. This data helps businesses understand what is working and what is not. For example, a company can analyze: By understanding these patterns, businesses can make better decisions like increasing stock for high-demand products, offering discounts on slow-moving items, or focusing marketing efforts on best-selling products. As a result, companies can reduce losses and increase overall profit. 2. Understanding Customer Behavior from Website or Social Media Data Customer behavior analysis focuses on understanding how users interact with a website or social media platform. Every click, like, comment, share, or visit creates data that shows what customers are interested in. For example, businesses can analyze: This data helps companies understand customer preferences and problems. If users leave a website without completing a purchase, businesses can improve the design, content, or user experience. Understanding customer behavior leads to better engagement, higher conversions, and stronger customer relationships. 3. Predicting Trends Using Past Data Predicting trends means using historical data (past records) to estimate what might happen in the future. Data Science identifies patterns and repeated behaviors in old data to make accurate predictions. For example, companies can predict: If past data shows that a product’s demand increases every year during a particular season, the company can prepare in advance by increasing production, inventory, and marketing. Trend prediction helps businesses plan better, reduce risks, and stay ahead of competitors. 2. Is Data Science Only for Engineers? (Myth vs Reality) This is one of the biggest myths. Reality: Companies value insights and decision-making skills, not just technical degrees. 3. Common Coding Fears Among Non-Tech Students Many non-tech students feel nervous about coding because they come from backgrounds where programming was never taught, which often creates self-doubt and fear even before they start learning. “I Have Never Done Coding Before” Many non-tech students feel scared because they have never written a single line of code in their academic life. This fear usually comes from the belief that coding must be very complex and technical. However, in Data Science, beginners start from the very basics, such as understanding simple commands and logic. Not having a coding background does not mean you cannot learn it. In fact, many successful data professionals started with zero coding knowledge and learned step by step. “Python Looks Difficult” Python often looks difficult to beginners because they see complex code examples online or hear others talk about advanced programming. In reality, Python is one of the easiest programming languages to learn, especially for non-tech students. It uses simple, English-like words, which makes it easier to read and understand. When Python is taught using real-life data examples instead of theory, it becomes much less intimidating and more practical. “My Math Is Weak” Another common fear is having weak mathematics skills. Many students think Data Science requires advanced mathematics or complex formulas. In reality, beginner-level Data Science uses only basic math concepts such as percentages, averages, and simple comparisons. The focus is more on understanding patterns and trends rather than solving difficult equations. With regular practice, even students who are not confident in math can perform well in Data Science roles. The Truth About Beginner-Level Coding in Data Science The truth is that beginner-level Data Science requires only very basic coding, and this coding is learned slowly and gradually through practice. Students are not expected to write complex programs at the start. Instead, they begin with small tasks like reading data, making simple calculations, and creating basic reports or charts. As confidence grows, coding skills improve naturally. With consistent hands-on practice and real-world examples, coding fear reduces over time, making Data Science accessible even for non-tech students. 4. Skills You Already Have That Help in Data Science As a non-tech student, you already have useful skills such as: Logical Thinking Logical thinking is the ability to break a big problem into smaller, manageable steps and analyze it clearly. In Data Science, this skill helps you understand what the data is saying and why certain patterns appear. For example, if sales suddenly drop, logical thinking helps you check factors like season, pricing, or customer behavior instead of guessing. Even without coding knowledge, logical thinking allows you to ask the right questions, connect data points, and make decisions based on facts rather than assumptions. This skill is one of the strongest advantages non-tech students already have. Basic Math (Percentages, Averages) Basic math plays an important role in understanding and analyzing data. Concepts like percentages help you measure growth, decline, or performance, while averages help you understand overall trends. For example, calculating average sales, conversion rates, or customer spending gives a clear picture of performance. You do not need advanced mathematics at the beginner level. These simple calculations are enough to draw meaningful conclusions and support data-driven decisions in most entry-level Data Science roles. Excel or Spreadsheet Knowledge Excel
Career Opportunities After LearningPython & R: Roles, Growth & Salaries

In today’s data-driven world, Python and R have become two of the most powerful and in-demand programming languages. From startups to global enterprises, organizations rely on data to make smarter decisions—and skilled professionals who can analyze, visualize, and interpret this data are in high demand.Learning Python and R opens the door to multiple high-growth career paths in data analytics, data science, machine learning, and business intelligence. This blog explores the top career opportunities, role responsibilities, growth potential, and salary expectations after mastering Python and R. Why Python & R Are Career-Defining Skills in the ModernTech Landscape Introduction: Skills That Shape the Future of Work In today’s rapidly evolving digital economy, data has become the backbone of decision-making across industries. Organizations no longer rely on intuition alone; they depend on data-driven insights to optimize operations, predict trends, improve customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge. At the center of this transformation are two powerful programming languages—Python and R. Together, they have emerged as career-defining skills for professionals aiming to build a strong, future-ready career in technology, analytics, and artificial intelligence. Python and R are not just tools; they are enablers of innovation. From startups to global enterprises, these languages empower professionals to convert raw data into meaningful intelligence. Mastering them opens doors to diverse roles, industries, and long-term growth opportunities. Understanding Python: The Backbone of ModernTechnology Python’s Versatility Across Domains Python has gained massive global adoption due to its simplicity, readability, and versatility. It is widely used for data analysis, automation, machine learning, artificial intelligence, web development, and cloud-based applications. Its extensive ecosystem of libraries—such as Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch—allows professionals to handle complex tasks efficiently and at scale. What makes Python particularly valuable is its ability to integrate seamlessly with other technologies. Whether it is working with databases, cloud platforms, APIs, or big data frameworks, Python adapts effortlessly, making it a preferred choice for organizations building modern digital solutions. Python in Real-World Business Applications In practical business environments, Python is used to automate repetitive tasks, process massive datasets, develop predictive models, and deploy AI-driven solutions. Companies rely on Python to optimize supply chains, detect fraud, personalize marketing campaigns, improve healthcare diagnostics, and enhance financial forecasting. This widespread applicability makes Python a foundational skill for professionals across technical and non-technical roles. The Power of R: Precision in Statistics and Research R as a Specialized Tool for Data Science While Python offers broad flexibility, R excels in statistical analysis, data modeling, and research-based insights. It is particularly favored by statisticians, data scientists, researchers, and analysts who work with complex datasets and require deep analytical accuracy. R provides advanced statistical techniques, hypothesis testing, regression modeling, and data visualization capabilities that are critical in research-driven environments. Industries such as healthcare, finance, pharmaceuticals, academia, and market research heavily rely on R for evidence-based decision-making. Its ability to produce high-quality visualizations and interpretable statistical outputs makes it indispensable where precisionmatters most. R’s Role in Evidence-Based Decision Making Organizations use R to analyze clinical trial data, assess financial risks, evaluate market behavior, and validate business strategies. The insights generated through R help leaders make informed decisions backed by statistical confidence rather than assumptions. For professionals, this means gaining credibility as someone who can translate data into reliable, actionable conclusions. Why Python and R Together Create a CompetitiveAdvantage Complementary Strengths for End-to-End Data Solutions Individually, Python and R are powerful; together, they create a comprehensive skill set that makes professionals highly versatile. Python handles data collection, preprocessing, automation, and machine learning efficiently, while R provides depth in statistical analysis and research validation. This combination allows professionals to manage the entire datalifecycle—from raw data to strategic insights. Employers increasingly value candidates who can switch between tools based on business needs. A professional proficient in both Python and R can collaborate effectively with cross-functional teams, bridge gaps between engineering and analytics, and deliver solutions that are both scalable and statistically sound. What Companies Expect from Data-Driven Professionals Handling and Cleaning Large DatasetsModern organizations generate enormous volumes of data from multiple sources, including customer interactions, IoT devices, transaction systems, and digital platforms. Companies expect professionals to efficiently collect, clean, structure, and manage this data. Python and R provide robust tools for data wrangling, ensuring accuracy, consistency, and reliability before analysis begins. Performing Advanced Statistical AnalysisBeyond basic reporting, businesses require deeper analysis to identify patterns, correlations, and trends. Professionals skilled in Python and R can apply statistical techniques to uncover insights that drive strategic decisions. This capability is essential for roles in data science, analytics, research, and business intelligence. Building Predictive and Machine Learning ModelsOne of the most valuable applications of Python and R is predictive modeling. Organizations use these models to forecast demand, predict customer behavior, optimize pricing, and reduce risks. Professionals who can design, train, and evaluate predictive models are seen as high-value assets in today’s competitive job market. Communicating Insights Clearly and Effectively Technical skills alone are not enough. Companies seek professionals who can communicate insights clearly to stakeholders who may not have a technical background. Python and R enable the creation of meaningful visualizations, dashboards, and reports that translate complex data into understandable narratives. This ability to connect data with business strategy is what truly defines a successful professional. Industry-Wide Demand for Python and R Skills Applications Across Multiple Sectors Python and R are in demand across a wide range of industries, including IT, finance, healthcare, marketing, e-commerce, manufacturing, logistics, and consulting. Whether it is optimizing production processes, improving patient outcomes, enhancing customer targeting, or driving digital transformation, these skills are universally relevant. Career Roles Enabled by Python and R Professionals with expertise in Python and R can pursue diverse career paths such as Data Analyst, Data Scientist, Machine Learning Engineer, Business Analyst, AI Specialist, Research Analyst, and Automation Engineer. These roles not only offer strong compensation but also long-term career stability and growth. Python & R as Long-Term Career Investments Staying Relevant in a Rapidly Changing Job Market Technology continues to evolve, but
ChatGPT, Gemini & Beyond: Why AI Certifications Are Creating the Hottest Career Opportunities in 2026

Artificial Intelligence is no longer a future concept — it’s the present reality shaping careers across industries. Tools like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Copilot, and other generative AI platforms are redefining how businesses operate, make decisions, and scale faster than ever. As AI adoption accelerates, new career paths are opening up, and professionals with the right AI skills and certifications are seeing exponential growth.Let’s break down how Generative AI is creating career opportunities — and why AI certifications will matter more than ever in 2026. How Generative AI Is Transforming Careers Generative AI is impacting far more than just content creation. It is becoming a core driver of automation, intelligence, and strategic decision-making across industries. Organizations are increasingly leveraging AI-powered tools to automate repetitive tasks, analyze vast datasets, generate insights, and improve operational efficiency. This technological shift is transforming traditional job roles, pushing professionals toward more strategic, analytical, and creative responsibilities, where human judgment, innovation, and leadership are combined with AI capabilities. Industries such as marketing, finance, healthcare, education, and technology are rapidly adopting Generative AI to remain competitive and deliver superior outcomes. In marketing, AI helps automate content creation, personalize campaigns, and analyze customer behavior. In finance, AI tools enable predictive analytics, fraud detection, and optimized investment strategies. Healthcare professionals are using AI to analyze medical data, assist in diagnostics, and improve patient outcomes, while education institutions leverage AI to personalize learning experiences and automate administrative tasks. Technology companies are integrating AI into software development, predictive modeling, and data-driven solutions to accelerate innovation. For professionals, understanding how to work alongside AI tools has become a critical skill that provides a competitive edge in the job market. AI is enabling individuals to focus on higher-value work, such as creative problem-solving, strategic planning, and decision-making, while automating repetitive or time-consuming tasks. This transition is also creating new roles, including AI content specialists, AI consultants, automation experts, data analysts, and AI project managers — roles that were rare or non-existent a few years ago. Generative AI is not only improving efficiency and productivity, but it is also fostering faster innovation, smarter decision-making, and personalized solutions across organizations. By enabling professionals to analyze trends, predict outcomes, and optimize workflows, AI is redefining the way work gets done. It is also encouraging professionals to upskill, adapt, and explore new career paths in AI-driven environments. Rather than replacing jobs, AI is enhancing human capabilities, redefining careers, and creating abundant opportunities for future-focused professionals. Those who embrace AI, learn to integrate it into their work, and earn recognized certifications are positioning themselves as strategic assets in the modern workforce. By combining human creativity and judgment with AI efficiency and intelligence, professionals can drive measurable business impact, innovate faster, and secure roles that are both high-value and future-ready.In essence, Generative AI is not just a tool—it is a career accelerator that empowers professionals to stay relevant, innovate continuously, and thrive in an AI-driven economy. 1. AI Content & Creative Automation From marketing copy and video scripts to design prompts and brand storytelling, AI-powered content roles are booming across industries. Businesses are increasingly using Generative AI to produce high-quality content at scale while maintaining brand consistency. Content creators, marketers, and designers are now working alongside AI tools to accelerate production, enhance creativity, and streamline workflows. AI is helping teams generate fresh ideas, optimize messaging, and personalize content for diverse audiences across multiple channels. This shift is not replacing creative professionals; rather, it is empowering them to focus on higher-level strategy, conceptual thinking, and storytelling, which are uniquely human skills. Skills like prompt writing, content optimization, AI tool management, and interpreting AI-generated analytics are becoming essential for anyone aiming to thrive in creative roles. Professionals who master these skills can increase output quality, improve audience engagement, and reduce turnaround times, making them invaluable assets in a competitive digital landscape. AI is now being used to automate repetitive content tasks such as: Drafting multiple copy variations for campaigns Resizing images and videos for different platforms Editing video snippets and audio overlays Generating design mockups or visual concepts By handling these routine tasks, AI frees creative professionals to focus on innovation, storytelling, and strategic planning, ensuring campaigns are not just produced faster but are also more effective, personalized, and engaging. In addition, businesses are integrating real-time AI analytics into creative workflows. This allows teams to track content performance continuously, understand audience behavior, and adjust strategies on the fly. Professionals who can blend creative expertise with AI analytics can iterate campaigns more effectively, maximize engagement, and deliver measurable results, giving brands a significant advantage in saturated markets. AI-driven creative automation is also creating entirely new career paths, including roles such as: AI Content Strategist – overseeing content strategy powered by AI insights AI Design Coordinator – managing design workflows using generative AI tools Generative AI Creative Consultant – advising brands on AI-driven creative solutions AI Marketing Analyst – leveraging AI to measure campaign performance and optimize outputs Individuals who combine creativity with AI proficiency are in high demand, experiencing better career growth, and gaining opportunities to lead innovative, cutting-edge campaigns. Furthermore, as AI continues to evolve, creative professionals who adapt quickly and integrate AI into their workflows will be the ones driving industry trends, thought leadership, and innovation in content creation.Ultimately, AI is not just a tool—it’s a transformative force in the creative industry. Professionals who embrace AI-driven content automation gain the ability to deliver more impactful campaigns, enhance efficiency, and stand out in a crowded market, opening doors to a wide range of exciting, future-ready careers that combine strategy, creativity, and technology. 2. Business Intelligence & Data-Driven Strategy AI tools now analyze massive datasets in minutes, helping businesses predict trends and make smarter decisions. Organizations are using AI-powered analytics to uncover patterns, customer behavior, and market opportunities that were previously hard to identify. Data-driven insights are now shaping business strategies, from pricing and marketing to operations and product development. Professionals who can interpret AI-generated data are becoming critical decision-makers.
AI, Analytics & Automation: Where Data Science Fits In

The Skill That Will Define Careers in 2026 and Beyond The world is entering a decisive phase where data is no longer just information—it is intelligence. As businesses move rapidly towards AI-driven decisions, predictive analytics, and automated systems, Data Science has become the backbone connecting AI, Analytics, and Automation. In the coming years, especially from 2026 onward, organizations will not ask whether to use data science—but how fast they can adopt it. What Is Data Science in the AI & Automation Era? Data Science has emerged as one of the most powerful disciplines shaping the modern digital world. In an era dominated by Artificial Intelligence and Automation, data is no longer just information stored in systems; it is the fuel that drives intelligence, decision-making, and autonomous actions. Data Science is the bridge that converts raw, unstructured data into meaningful insights, predictive intelligence, and automated outcomes. At its core, Data Science is the discipline that combines statistics, mathematics, computer science, and domain knowledge to extract value from data. In today’s ecosystem, its role has expanded far beyond reporting and dashboards. Data Science now enables machines to learn, businesses to predict, and systems to act independently with minimal human intervention. The Evolution of Data Science in the Digital Age Data Science did not begin with AI. Initially, organizations relied on basic data analysis to understand historical performance. Reports, spreadsheets, and descriptive analytics helped answer simple questions about what had already happened. As data volumes grew and computing power increased, organizations realized that data could do more than describe the past. The evolution of Data Science introduced predictive and prescriptive capabilities. Instead of asking what happened, businesses began asking what will happen and what should be done next. This shift marked the foundation of modern AI and automation systems, where data-driven intelligence became a strategic advantage rather than a support function. Data Science as the Foundation of Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence does not exist independently of data. Every AI system, whether it is a recommendation engine, chatbot, fraud detection model, or self-driving system, depends on data science methodologies to function effectively. Data Science provides the processes through which machines learn patterns, relationships, and behaviors from data. Through techniques such as machine learning, deep learning, and statistical modeling, Data Science enables AI systems to recognize trends, make predictions, and continuously improve their performance. Without clean, structured, and well-analyzed data, AI would lack the intelligence required to make accurate decisions. In simple terms, AI thinks, but Data Science teaches it how to think. The Role of Data Science in Analytics Analytics is often confused with Data Science, but analytics represents only one dimension of it. Analytics focuses on interpreting data to uncover patterns, trends, and insights that humans can understand and act upon. Data Science, on the other hand, includes analytics while extending into prediction, optimization, and automation. Data Science empowers analytics by providing advanced statistical techniques, feature engineering, and modeling frameworks. It transforms raw datasets into structured insights that guide strategic planning, performance measurement, and business intelligence. In organizations today, analytics teams rely heavily on data science principles to ensure accuracy, scalability, and relevance of insights. Analytics explains what is happening and why it is happening, but Data Science builds the engine that makes such explanations possible. Automation and the Rise of Data-Driven Decision Making Automation represents the action layer of modern digital systems. Automated systems execute decisions without continuous human involvement, whether it is approving a transaction, adjusting inventory levels, triggering alerts, or personalizing customer experiences. These decisions are only as good as the data that powers them. Data Science enables automation by translating insights and predictions into decision logic. It provides the rules, thresholds, and models that automated systems rely on to act accurately and efficiently. In advanced environments, data science models continuously learn from new data, allowing automation systems to adapt to changing conditions in real time. Automation acts, but Data Science decides how and when it should act. The Interconnection Between AI, Analytics, and Automation In the modern ecosystem, AI, analytics, and automation are not separate silos. They function as an integrated system, and Data Science sits at the center of this integration. AI depends on data science to learn and predict. Analytics depends on data science to interpret patterns and trends. Automation depends on data science to execute decisions with confidence. This interconnected relationship allows organizations to move from reactive decision-making to proactive and autonomous operations. Data Science ensures that intelligence flows seamlessly from data collection to insight generation and finally to automated execution. In simple terms, AI thinks, analytics explains, automation acts, and Data Science powers all three. Key Components of Data Science in the AI Era Modern Data Science involves multiple components working together to deliver intelligence and automation. Data collection ensures that relevant and high-quality data is captured from diverse sources such as sensors, applications, user interactions, and transactions. Data processing cleans and structures this information to make it usable. Modeling and analysis apply statistical and machine learning techniques to extract insights and predictions. Deployment and monitoring ensure that models operate reliably in real-world environments and continue to improve over time. Each of these components plays a critical role in enabling AI-driven systems and automated workflows. Data Science and Predictive Intelligence One of the most powerful contributions of Data Science is predictive intelligence. Instead of relying solely on historical data, organizations can use data science models to anticipate future outcomes. These predictions enable businesses to plan proactively, reduce risks, and seize opportunities before they arise. Predictive intelligence is used across industries, from forecasting demand and detecting fraud to predicting equipment failures and customer behavior. In each case, Data Science transforms uncertainty into actionable foresight, empowering both humans and machines to make informed decisions. Ethical and Responsible Use of Data Science As Data Science becomes more deeply embedded in AI and automation, ethical considerations gain increasing importance. Decisions driven by data science models can significantly impact individuals, businesses, and societies. Bias, data privacy, transparency, and accountability
Top 10 Vulnerabilities Cybercriminals Exploit —

And How Ethical Hackers Stop Them In today’s hyper-connected digital world, cyber threats evolve every day. Hackers are more sophisticated, smarter, and constantly probing for weak spots in systems — but ethical hackers work just as hard (if not harder) to safeguard businesses before damage occurs. At Pinaki IT Consultant Pvt. Ltd., we believe strong cybersecurity isn’t just a defense — it’s a proactive shield built on understanding vulnerabilities, testing systems relentlessly, and leveraging cutting-edge technologies like AI for real-time threat intelligence. In this article, we’ll explore: ✔ The Top 10 vulnerabilities cybercriminals exploit✔ How ethical hackers identify and fix them✔ How companies implement defenses✔ How AI enhances cybersecurity What Is a Vulnerability? A vulnerability is any flaw or weakness hidden within software, hardware components, networks, or even day-to-day operational processes that can be misused by attackers. These weaknesses create openings that allow unauthorized access, data theft, service interruptions, or complete system manipulation. In today’s digital landscape, no industry is fully immune — whether it’s finance, healthcare, retail, education, or government, every sector carries potential blind spots that cybercriminals actively look for. This is where ethical hackers play a crucial role. They identify these weak points before malicious actors do, helping organizations strengthen their systems, patch vulnerabilities, and build a safer, moreresilient digital environment. Understanding the Role of Ethical Hackers Ethical hackers — sometimes called white-hat hackers or cybersecurity analysts — play a crucial role in identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks long before they turn into threats. Unlike cybercriminals, they work under legal authorization and follow strict guidelines. Their job is to mimic attackers, uncover vulnerabilities, and provide actionable insights thatstrengthen the organization’s overall security posture. Ethical hackers bridge the gap between potential weaknesses and the strong, resilient systems needed to protect sensitive data, operations, and brand trust. They use a variety of structured methodologies to uncover how an attacker might infiltrate a system. Each technique serves a unique purpose, allowing businesses to see their digital environment through different threat perspectives — whether technical, procedural, or human. This holistic approach ensures that no potential risk is left hidden beneath the surface. Penetration Testing (Pentesting) Simulating Real-World AttacksPenetration testing is one of the most powerful tools ethical hackers use to understand an organization’s true security strength. It involves simulating real-world cyberattacks on networks, applications, servers, and devices. The goal is not just to find vulnerabilities but to demonstrate how deep an attacker could go if those vulnerabilities were exploited. Pentesting helps organizations recognize whether their current security controls are truly effective or simply giving a false sense of protection. Identifying Weak Points Before Criminals DoEvery system, no matter how advanced, carries risks. Penetration tests uncover security gaps such as misconfigurations, outdated software, poor authentication practices, exposed APIs, or insecure data pathways. Ethical hackers use step-by-step, attacker-like methodologies to explore these loopholes and assess how far they can penetrate. This process reveals not just what is vulnerable, but how an actual breach could unfold — making it one of the most realistic security exercises a business can invest in. Delivering Actionable SolutionsAfter completing the test, ethical hackers compile detailed reports explaining the vulnerabilities found, the severity of each issue, and how they can be fixed. This empowers businesses to prioritize repairs, allocate budgets better, and strengthen their systems strategically rather than blindly. Pentesting is not just a test — it’s a pathway toward stronger, smarter, and more resilient cybersecurity. Vulnerability Assessments Scanning for Weaknesses Across the Entire Digital InfrastructureWhile pentesting focuses on attack simulation, vulnerability assessments take a more systematic and wide-angle approach. Ethical hackers perform automated and manual scans across networks, devices, applications, and cloud environments to detect any potential flaw that could lead to a breach. This assessment covers everything from unpatched software to weak passwords, misconfigured firewalls, insecure ports, and outdated libraries. Recognizing Risks Before They Become ThreatsVulnerability assessments help organizations maintain constant awareness of their security posture. New vulnerabilities surface daily — from zero-day exploits to evolving malware strains. Ethical hackers continuously analyze these trends and correlate them with the company’s systems to determine which new weaknesses could have an impact. This process ensures that organizations always stay one step ahead of attackers. Prioritizing Fixes Based on SeverityNot all vulnerabilities pose the same level of danger. Ethical hackers classify them based on criticality, potential impact, and exploitability. This allows security teams to fix the most dangerous risks first and ensure resources are used effectively. Vulnerability assessments are a continuous process — essential for maintaining long-term security and preventingunnoticed risks from piling up. Security Audits Evaluating Compliance, Controls & Best PracticesSecurity audits are comprehensive examinations of an organization’s cybersecurity policies, procedures, and technical configurations. Ethical hackers review everything — from access control to data protection protocols — to ensure the company meets compliance standards such as ISO, GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and more. Ensuring Strong Governance Across All DepartmentsUnlike pentesting, which is highly technical, security audits also evaluate non-technical aspects of cybersecurity. This includes employee behavior, documentation quality, incident response readiness, backup policies, and physical security measures. Ethical hackers analyze whether workflows align with industry standards and whether every departmentfollows necessary security practices. Building Long-Term, System-Level SecurityThrough these audits, organizations gain clarity on where they stand and what needs improvement. Ethical hackers provide detailed recommendations that strengthen governance, enhance internal processes, and create a more resilient security culture. Security audits lay the foundation for ongoing protection — not just technical fixes butinstitutional improvements. Social Engineering Tests Testing the Human Side of SecurityTechnology may be strong, but humans are often the weakest link. Social engineering tests are designed to measure how employees respond to real-world psychological manipulation attempts. Ethical hackers mimic attackers by sending phishing emails, impersonating internal staff, making scam phone calls, or attempting unauthorized physical access. Understanding Employee Awareness & Training NeedsThese tests reveal whether employees unknowingly click suspicious links, share sensitive data, or fail to verify identities. Ethical hackers don’t conduct these tests to blame staff — but to diagnose training gaps, improve awareness, and prevent human
Why Every Working Professional Must Learn AI& Data Skills (Regardless of Their Job Role)

In today’s fast-changing digital world, every major industry — whether it’s finance, marketing, HR, healthcare, logistics, supply chain, ed-tech, retail, e-commerce, or customer service — is being reshaped by the combined force of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Science. The impact is so deep and widespread that no job role, department, or business model can afford to ignore it anymore. Processes that once required heavy manpower, long hours, and complex decision cycles are now being executed faster, smarter, and with far greater accuracy thanks to AI-driven insights and automation. The truth is simple and undeniable: AI is not replacing people… AI-powered professionals are replacing those who don’t upgrade. Companies are not looking for just employees anymore — they want efficient employees, data-driven problem solvers, and professionals who can work smarter, not just harder. Whether you’re a fresher entering the job market, a mid-level employee trying to grow, a senior manager leading teams, or even a business owner trying to scale operations — AI and data skills have become the new baseline for future career growth. The shift is already visible everywhere. Businesses that adopt AI move faster than their competitors. Teams that understand data make better decisions. Professionals who automate repetitive tasks achieve higher productivity and gain more opportunities. In a world where technology evolves daily, the biggest career risk today is sticking to old methods while the industry moves ahead. That is why upskilling is no longer a luxury — it is a survival strategy. Building AI and data skills today doesn’t just prepare you for future jobs; it empowers you to stay relevant, confident, and irreplaceable in your field. AI & Data Skills Are Now Required in Every Job Role The Era of Universal Digital Transformation The modern workplace has undergone one of the most dramatic shifts in human history. For decades, technology evolved steadily, staying largely within the domains of IT experts, programmers, engineers, or data scientists. But the arrival of artificial intelligence and data-driven technologies has completely transformed this landscape. Today, AI is not simply an add-on or a luxury; it has become the backbone of nearly every industry, every business function, and every professional role. Whether in small startups or global enterprises, the fundamental expectation is clear: employees must know howto work alongside intelligent digital tools. This shift has created a revolution in job requirements, placing AI literacy and data understanding at the center of future skills. AI no longer exists as a specialized function tucked away in server rooms. It is now embedded in the tools we use daily, the platforms we manage, the customer interactions we handle, and the decisions we make. Employees today cannot rely on traditional experience alone; they must be able to interpret data, automate tasks, and understand intelligent systems thatinfluence business operations. What was once a niche skill expected from a select few is now a universal requirement across departments — from marketing to sales, finance to operations, HR to healthcare, and even education. The modern professional is expected to be a hybrid: someone who combines human expertise with digital capability. The Rise of Intelligent Tools Across Departments Artificial intelligence has moved closer to the core of every business function. For marketers, AI helps automate content, optimize ads, and predict customer behavior. For sales teams, AI-powered CRM systems analyze large volumes of customer data and provide insights that were impossible to see manually. For HR professionals, AI helps with resume screening, employee retention analysis, and workforce planning. For finance teams, AI tools detect fraud, forecast budgets, and track anomalies in real time. Even sectors traditionally driven by manual processes, such as operations, logistics, and healthcare, are now deeply dependent on AI-driven automation and analytics. The introduction of these tools has not reduced the importance of human judgment; rather, it has amplified it. AI provides clarity, speed, and efficiency, but it still needs human oversight, direction, and contextual decision-making. As a result, professionals can no longer afford to ignore these systems or remain dependent on outdated workflows. This growing ecosystem of intelligent platforms has made it essential for every employee to understand how AI operates, how data is processed, and how analytical insights are used. Without this knowledge, employees risk falling behind or becoming lessvaluable in an increasingly competitive market. Marketing: A Completely Transformed Landscape Marketing has experienced one of the most dramatic AI transitions of all industries. What was once a heavily manual, intuition-driven field is now powered by algorithms capable of analyzing millions of data points at lightningspeed. AI tools create social media content, generate ad copies, design personalized email campaigns, and even identify ideal audiences with astonishing accuracy. Digital marketers use AI-driven ad optimization systems that track real-time performance and adjust campaigns automatically, ensuring maximum ROI with minimal human intervention. This shift means marketers are no longer simply storytellers or creative thinkers. They must now understand how AI models predict user behavior, how algorithms determine ad placements, and how analytics dashboards translate massive data sets into actionable insights. The modern marketer is expected to be data-savvy, tech-aware, and comfortable with automationtools. Those who understand AI not only work more efficiently but also create stronger, more personalized customer experiences. Sales: Driven by Predictions and Buyer Intelligence Sales teams today operate in a world where data drives nearly every decision. AI-powered CRM systems now track customer interactions, analyze communication patterns, and predict which leads are more likely to convert. Instead of manually sorting through hundreds of contacts, sales professionals rely on intelligent scoring systems that highlight high-potential prospects. AI also helps personalize pitches, recommend follow-up strategies, and identify emerging market opportunities. The sales process has shifted from guesswork to science. A modern salesperson must understand these tools to work effectively. The ability to interpret CRM insights, leverage AI recommendations, and analyze customer behavior data is now part of the core job requirement. Without these skills, sales professionals risk losing deals to competitors who use AI-driven insights to build deeper, more intelligent customer relationships. Human Resources: Automation for Better
Humans + AI = Superpower!Why the Future Belongs to Human–AICollaboration
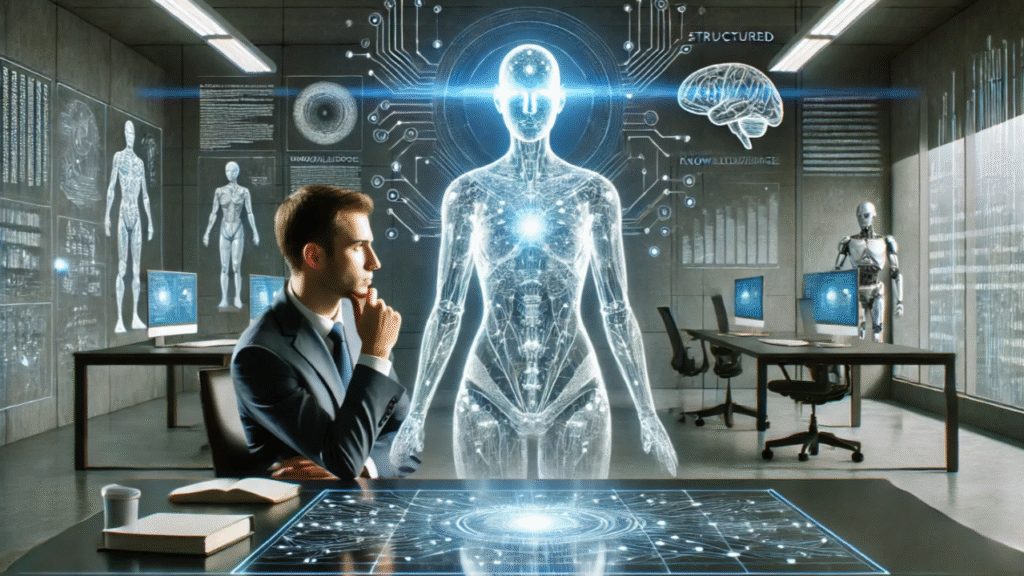
For years, the world kept debating whether AI would replace humans and whether machines would eventually take over our jobs. But today, the truth is clearer than ever: it’s not Humans vs AI — it’s Humans with AI. When human intelligence, creativity, intuition, and emotion come together with the speed, precision, and analytical power of artificial intelligence, something extraordinary happens. We unlock a superpower that neither side can achieve alone. This is the beginning of a new era — a future shaped by collaboration, innovation, and limitless possibilities. Welcome to the age where humans don’t compete with AI… they rise higher with it. The Real Future: Human IntelligenceAmplified by Artificial Intelligence The Shift From Fear to Understanding For decades, the global conversation around technology has been dominated by a single anxiety-driven question: “Will AI replace humans?” This fear grew louder each time a breakthrough in automation or machine learning was announced, as though every innovation moved humanity one step closer to irrelevance. Yet, as we stand today in the most advanced phase of the digital revolution, the answer has become clearer than ever. AI is not here to replace humans; it is here to amplify what humans can do. The future is not a battlefield where humans and machines fight for dominance. Instead, it is a shared space where human intelligence and artificial intelligence merge to create something far greater than either could achieve alone. What once seemed like a threat is now revealing itself as an unprecedented opportunity to unlock new levels of creativity, problem-solving, and progress. What Humans Bring to the Equation Human intelligence is rich with qualities no machine can replicate — not because AI is limited, but because the human experience is infinitely complex. Emotion, intuition, imagination, empathy, and the ability to understand the unspoken layers of human life give people a depth that goes beyond data. A human mind can look at a challenge and not only calculate possibilities but also imagine entirely new realities. We feel, connect, dream, hesitate, reflect, and create meaning in everything we do. Humans understand context, cultural nuance, social behavior, and moral responsibility in a way no algorithm can. This is what allows leaders to inspire, artists to innovate, caregivers to heal, and strategists to envision long-term transformation. Our intelligence is not linear — it is emotional, spiritual, logical, and creative all at once. That multidimensional nature is what makes us unique and irreplaceable. What AI Adds to Human Potential Artificial intelligence brings a completely different kind of power — speed, scale, and precision. AI can process massive datasets in seconds, detect patterns invisible to the human eye, execute repetitive tasks with perfect consistency, and make predictions based purely on logic and data. It enhances accuracy, reduces error, accelerates workflows, and unlocks opportunities that were once limited by time and human capacity. AI does not get tired, overwhelmed, emotional, or distracted. It can operate continuously, learning from every new piece of information and refining its capabilities over time. This ability to analyze, automate, and optimize makes AI not a competitor but a powerful partner that extends what humans can achieve. By taking over the mechanical parts of work, AI frees humans to do what we do best — innovate, think, create, and connect. The Power of Combining Human and ArtificialIntelligence When human strengths and AI capabilities merge, a new form of hybrid intelligence emerges — one that is superior to either side alone. Human creativity guided by AI insights becomes more precise. Human decisions supported by AI analysis become stronger. Human empathy enhanced with AI-driven personalization becomes more impactful. On the other hand, AI becomes far more meaningful when directed by human purpose, emotion, and ethics. Together, they create a force that is smarter, faster, and more powerful than anything the world has seen before. This synergy is not the distant future — it is already shaping medicine, engineering, business, education, art, marketing, and every major field of innovation. When humans think and machines compute, ideas that once took months can now take minutes. Solutions that once felt impossible suddenly become achievable. The Future of Work, Innovation, and Business Growth The workplace of tomorrow will not be dominated by robots pushing humans aside. Instead, it will be a space where people use AI as naturally as they use smartphones today — as tools that expand their abilities and open new paths forward. Companies that embrace this collaboration will grow faster, innovate smarter, and operate more efficiently. Creativity will scale. Decision-making will strengthen. Customer experiences will become more personalized. Industries will be transformed not because AI replaces humans, but because AI empowers humans to operate at their highest potential. The future belongs to those who understand that AI is not a replacement but an amplifier — a catalyst that elevates human intelligence to extraordinary heights. A New Era of Human–Machine Partnership We are entering a time where the most successful individuals and organizations will not be the ones who fear AI, but the ones who embrace it as a partner. Human intelligence defines the direction; artificial intelligence accelerates the journey.Together, they unlock possibilities that were once unimaginable. The real future is not Humans vs AI. It is Humans with AI —working side by side, building, creating, healing, solving, and pushing the world into a new era of limitless possibilities. Why Humans Alone Aren’t EnoughAnymore Understanding the Pace of Today’s World In today’s world, we live inside a storm of information—an environment where the speed, scale, and complexity of daily operations far exceed anything humanity has ever witnessed before. Every second, billions of data points are generated across industries, platforms, devices, and consumer touchpoints. These data streams are not occasional; they are constant, endless, and overwhelmingly rich. They come from customer interactions, market fluctuations, browsing patterns, mobile usage behaviors, financial transactions, supply-chain movements, social sentiments, and thousands of micro-activities happening around the world simultaneously. What used to be a manageable flow of information has now turned into a massive ocean, expanding
